German small arms exports 2013 according to regions of recipient countries
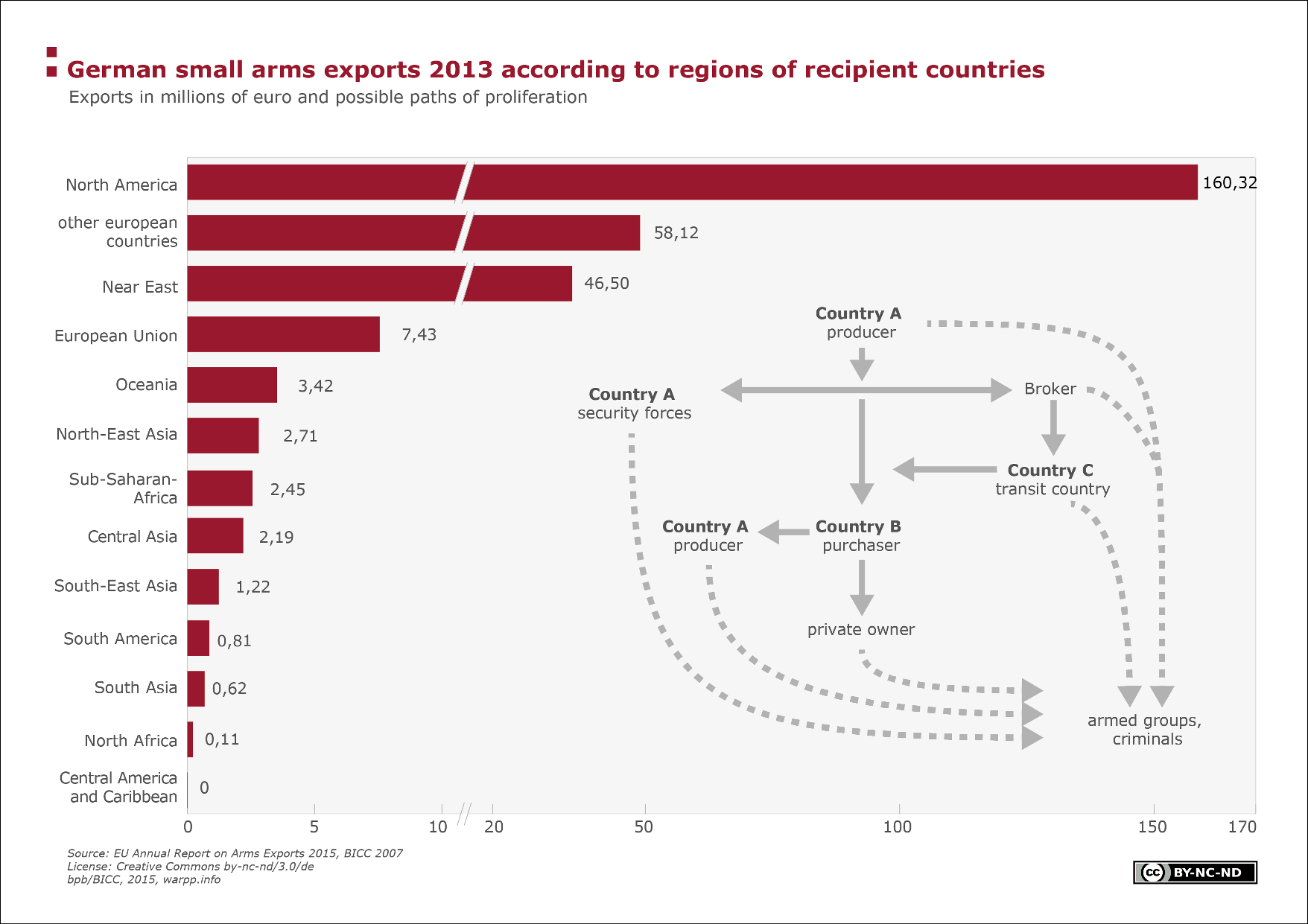
This graph shows the exports of German small arms in millions of euro as well as the paths for possible proliferation The data are broken down by recipient regions The largest small arms exports went to North America, followed by exports to non-EU European countries, closely followed by exports to the Middle East.
Facts
In 2013, Germany exported SALW worth 285,899,352 euro After the United States and Italy, it is the third-largest exporter in terms of value of goods The export of SALW is controlled in German law by the law on the control of weapons of war ('Kriegswaffenkontrollgesetz'). In EU law, the export of war materials is controlled by the EU Common Position 2008/944/CFSP. All member states must be informed of export licenses of war materials; these licenses ought to be granted in accordance with eight criteria.
Small arms are often used in non-state conflicts and are the weapons preferred by criminals and politically motivated groups. According to estimates, there are between 600 and 800 million firearms in the world. The fact that small arms are relatively cheap and easily available, they can be hidden and smuggled easily, are resistant against dirt and corrosion, extremely easy to maintain and have a long service life—even after many decades, they can still be operational—contributes to their high circulation. There are two reasons why Germany SALW are also available in areas of conflict: It is not legally binding to take the eight criteria of the Common Position into account and there are gaps in the existing regulatory mechanisms What started as a ‘legal’ export can easily end up in black or ‘grey’ markets.
Terms, notes on methodology or reading aids
Small arms and light weapons are portable arms with a calibre of up to 100mm. They range from revolvers and pistols, assault rifles and machine guns to grenade launchers and MANPADS (man-portable air defence systems). Small arms are firearms that have been designed for the use by one person and have a calibre of up to 12.7 mm, while light weapons have a higher calibre (12.7 to 100 mm) and are operated by a team of two or three. Their acronym is SALW.
Other European countries: Albania, Andorra, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Holy See (Vatican City State), Iceland, Kosovo (UNSCR, 1244/99), Liechtenstein, Macedonia, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, Norway, Russia, San Marino, Serbia, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine
European Union: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark (Denmark, Greenland, Faeroe Islands), Estonia, Finland, France (French Polynesia, Mayotte and New Caledonia), Germany, Greece, Great Britain (Great Britain, Bermuda, Cayman Islands, Channel Islands, Gibraltar, Saint Helena, Turks and Caicos Islands), Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Kroatia, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands (the Netherlands, Aruba, Netherlands Antilles), Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden
Middle East: Bahrain, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestinian Autonomous Territories, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, United Arab Emirates, Yemen
North Africa: Algeria, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia
North America: Canada, United States
North East Asia: China (Mainland, Hong Kong, Macao), Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan
Oceania: Australia, Federal States of Micronesia, Fiji, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Nauru, New Zealand, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, Vanuatu
Sub Sahara Africa: Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Cape Verde Islands, Central Africa, Chad, Comoros, Côte d‘Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea. Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, , Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, São Tomé and Príncipe, Senegal, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Swaziland, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe
South America: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Ecuador, Guyana, Colombia, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela South
Asia: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka South East Asia: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia/Burma, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Timor-Leste, Vietnam Central
America and Caribbean: Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominica, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Grenada, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, , Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago Central
Central Asia: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan
Datenquellen
Rüstungsexportberichte der EU (EU Arms Export Reports) 1999-2014 In 1998, in the framework of the Common Foreign and Security Policy of EU Member States, a code of conduct for arms exports was adopted that is not legally binding. In 2008, this code of conduct was integrated into the Common Position No 944. It stipulates that all members have agreed to integrate it into national law. Core element of the Common Position are eight criteria regarding arms exports licenses and the commitment to present an annual arms exports report. The eight criteria lay down when trade or the movement of military goods and weapons is permitted. A final decision on whether it wants to finally permit the transfer of military technology, however, is up to each individual nation. These annual export reports are intended to improve transparency in arms deals. In these reports, each country lists its exports of military weapons and military equipment according to the country of destination. These goods are divided into 22 categories Small arms exports are recorded in category ML1 : "Smooth-bore weapons with a calilbre of less than 20mm, other arms and automatic weapons with a calibre of 12.7mm (calibre 0.50 inches) or less and accessories, as follows, as specially designed components therefor."
BICC (Bonn International Center for Conversion; Internationales Konversionszentrum Bonn) Das BICC ist eine unabhängige gemeinnützige Organisation, die sich für Frieden und Entwicklung einsetzt. Das Institut arbeitet an der konstruktiven Transformation von Konflikten, Abrüstung und Armutsbekämpfung. Das BICC entwickelt und betreibt seit 2012 in Kooperation mit dem Verifikationszentrum der Bundeswehr (ZVBw) den interaktiven Kleinwaffen-Guide. In dem Onlineprotal werden die wichtigsten Klein- und Leichtwaffen dargestellt. Neben technischen Details zu einzelnen Waffenarten und ihren verschiedenen Versionen, sowie Fotos und Skizzen von Markierungen, wird vor allem die globale Verbreitung einzelner Waffen gezeigt. Diese Details sollen bei einer schnellen Identifizierung von Waffen behilflich sein.